Since September 2019, Google treats the nofollow attribute as a hint rather than a directive. This means Google may choose to follow nofollow links and use them for ranking purposes – a significant shift from the original intent of the attribute.
NoFollow links have measurable SEO value. They help expose your brand, drive traffic to your site, contribute to overall engagement metrics, and can even help search engines discover and index your pages faster.
The myth that NoFollow links have zero SEO value is outdated. Google’s shift to treating nofollow as a “hint” in 2019 means these links can influence rankings, crawling, and indexing in ways they previously could not.
In this guide, you will learn what NoFollow links are, how they differ from standard links, how the sponsored and ugc attributes fit in, and how to work with these links in WordPress.
What are NoFollow links, actually?
NoFollow is an HTML attribute intended for links and serves to inform search engines that theoretically, “this link shouldn’t affect the ranking of the linked site,” to which you are linking, and I intentionally emphasize this with quotation marks at the start of this post.
This feature came into existence to minimize the impact of spam links (you can also disavow low-quality backlinks pointing to your site) and thereby improve the quality and relevance of search engine results.
There are two types of NoFollow. One is through the Robots Meta Tag – if it exists, the implication is that you’re asking search engines not to follow any links on that specific page.
You need to add this tag to the head of the page, and you can also add it through local settings for the page using the Yoast SEO plugin for WordPress. The tag looks like this:
<meta name=”robots” content=”nofollow” />The second is by adding the rel="nofollow" attribute to the link itself, and the implication is, as you probably already understand, to ask search engines not to follow that specific link only. Using this tag looks like this:
<a href=”http://www.google.com” rel=”nofollow”>Did you know? In the past, there wasn’t a convenient way to make a link a NoFollow link, and the only option available to site administrators was to instruct that all links on the page be NoFollow links.
Which types of links are NoFollow?
So, as you probably understood, any link with the NoFollow attribute is technically a NoFollow link. But in general, links coming from the following sources tend to be NoFollow links:
- Blog comments – rare are the blogs that allow follow links in comments, which is one of the main reasons the concept of NoFollow links was created.
- Social networks (for example, links shared on Facebook).
- Forums and user-generated content. There’s no real reason to invite Google to follow links like “Register here” or “Login to the system” – places where Google’s bots can’t reach and crawl. (See video in the comments).
- Specific blogs and news sites.
- Links from widgets and similar elements.
- Press releases.
- Unreliable content.
- Pay-per-click/advertising links – in order to prevent the impact of paid links on search results, a situation that negatively affects users, these links must be NoFollow links.
The sponsored and ugc Link Attributes
In September 2019, Google introduced two new link attributes alongside nofollow:
rel="sponsored"– for paid links, sponsored content, and affiliate links. Using this attribute is required to comply with Google’s guidelines. Failing to mark paid links can result in penalties.rel="ugc"– for links within user-generated content, such as comments and forum posts.
These attributes can be combined (e.g., rel="nofollow sponsored"). Google also announced at the same time that all three attributes – nofollow, sponsored, and ugc – would be treated as hints rather than strict directives.
For a detailed explanation of these attributes and their impact on SEO, refer to the post on Nofollow, Sponsored, and UGC link attributes.
Paid links that are not marked with rel="sponsored" or rel="nofollow" violate Google’s guidelines. This applies to both sides – the site placing the paid link and the site receiving it. Penalties can include loss of rankings or manual actions in Google Search Console.
In any case, if you noticed or not, on many popular sites, the following outgoing links all have the rel="nofollow" attribute:
- YouTube
- Quora
- Wikipedia
- Twitch
- Medium
- And generally on most sites of this type.
Where Did the Concept of NoFollow Come From?
Although NoFollow appeared in HTML4 specifications, the concept was not created by W3C. It was created through collaboration among three major search engine companies – Google, Yahoo, and Microsoft – along with several powerful blogging platforms during the early days of 2005.
The reason for this was that during the period preceding it, there was a surge of spam comments in blogs, precisely when the popularity of blogs on the internet was skyrocketing.
People realized that search engines regarded links as a measure of the linked site’s ranking, and unfortunately, people decided that commenting on others’ posts with a link to their own site was a quick way to gain higher search engine rankings.
This situation put pressure on those search engines, especially Google, to find a solution. The NoFollow feature is an integral part of this battle, and the underlying thought is clear – if credit is not given for comments, it’s likely that people will stop with that spam.
Check any blog you want and you’ll find that links in comments are marked as NoFollow links in 99% of cases.
How to Check if a Link is NoFollow?
How can you determine if a link is Follow or NoFollow? For those who are not familiar, you can go to Google Chrome’s menu, then Developer > View Source, perform a search (Edit > Find) for the word “nofollow,” and see the results as shown in the following image:
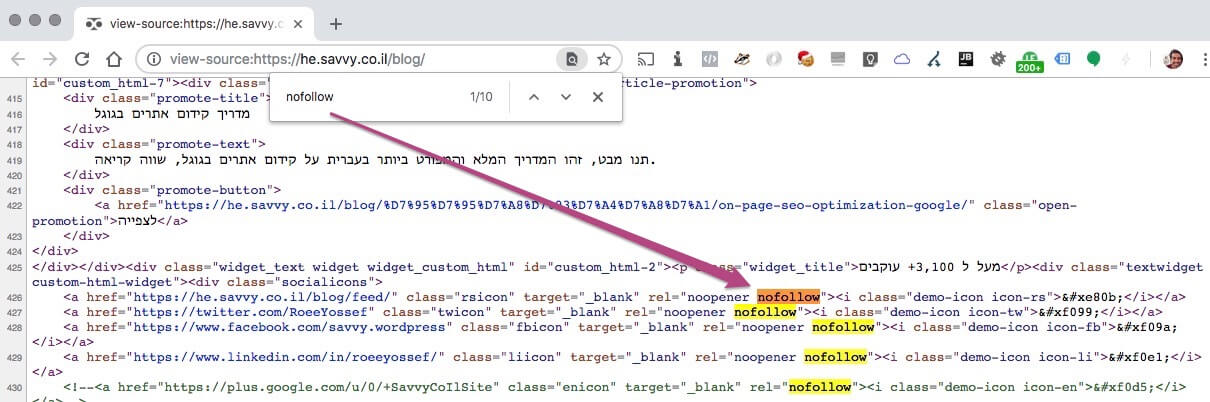
Alternatively, you can simply use Inspect Element by right-clicking the link in question and seeing if the tag is present. Of course, you can do this in other browsers as well.
What’s the Difference Between Standard Links and NoFollow Links?
As mentioned, NoFollow links are meant to indicate to search engines that the link should not be followed. The implication is that if a certain site links to your site with the NoFollow attribute, it does not pass on Link Equity (or the notorious “link juice”) to your site.
In other words, theoretically, the ranking of your site will not be directly affected by that link.
The correct approach is to add the NoFollow attribute only to links that are not relevant to the current content on your page that the user is viewing.
Beyond that, you should also add this attribute to links that people pay you for, which are usually not relevant in the context of the content.
On the other hand, “DoFollow links”, also known as standard links, indicate to search engines that they should be followed, and they pass on the coveted link equity.
These links serve as an indication to search engines that the content on your site is reliable and high-quality – a key factor in E-E-A-T evaluation – especially if the linking source has a strong profile.
The most effective way to provide a standard link to a specific site is by adding relevant keywords in the link text (anchor text).
These standard links have stronger impact from a search engine perspective if they appear in a context relevant to the link itself (meaning the text surrounding the link is relevant to the link itself).
By default, all links are “DoFollow links,” and you don’t need to do anything special to make a link like that. Additionally, anchor text does not have special value in NoFollow links, unlike standard links.
Do NoFollow Links TO Your Site Harm Your Ranking?
Quick answer? No. NoFollow links won’t affect your ranking.
However, there’s a small scenario that goes beyond the general rule as stated by Google. Imagine a somewhat hypothetical situation where you leave comments on every post on a specific site.
If you do this extensively and in an extreme manner, such that other users are already familiar with you and your comments fall into the category of “annoying” or spammy, Google might take minor actions and treat your link as spam. You can monitor your backlink profile in Google Search Console.
This is because it’s quite clear to everyone that your main goal is to divert traffic to your site through manipulative actions.
Do NoFollow Links FROM Your Site Harm Your Ranking?
In this case too, the answer is no. Perhaps this was the case many years ago when the concept of NoFollow emerged, but it’s not the case today.
Google has stated that there are three scenarios where you should use the NoFollow attribute:
- When you have any commercial relationship with the linked page, meaning links that pay you.
- When you didn’t create the link yourself, and from this, the link might not be reliable, like comments.
- If you’re linking to an unreliable site (for instance, when you’re providing a “bad” example in your content for demonstration purposes).
- In cases where you’re linking to administrative pages or similar ones that aren’t relevant to the searcher’s intent, like privacy policy/terms of service pages and login pages for certain management systems.
There’s also a discussion that Google pays special attention to sites where all outgoing links are marked as NoFollow and treats it as a sign of unnatural manipulation that can undermine your page’s credibility.
NoFollow as a “Hint” – What Changed in 2019
Before September 2019, when a link had the nofollow attribute, Google would not follow it and would not use it for ranking purposes. The attribute was a strict directive.
Since March 2020 (when the change fully took effect), Google treats nofollow as a hint. This means Google reserves the right to follow nofollow links and use them as a signal for ranking and crawling.
In practice, this has several implications:
- NoFollow links from high-authority sites may pass some ranking value.
- Google can use nofollow links for discovering and indexing new pages.
- Using nofollow on internal links for “PageRank sculpting” no longer works – the link equity simply evaporates rather than being redistributed.
Google’s John Mueller confirmed that nofollow links can still help with discovery and indexing. The “generally” qualifier in Google’s documentation is intentional.
NoFollow Links in WordPress Sites
While WordPress now provides a more straightforward way to add the rel="nofollow" attribute directly within the Gutenberg editor, this was not always the case.
Mark a link as nofollow in Gutenberg
With the recent updates to Gutenberg, the WordPress block editor, it’s now easier to add rel="nofollow" directly from the link UI:
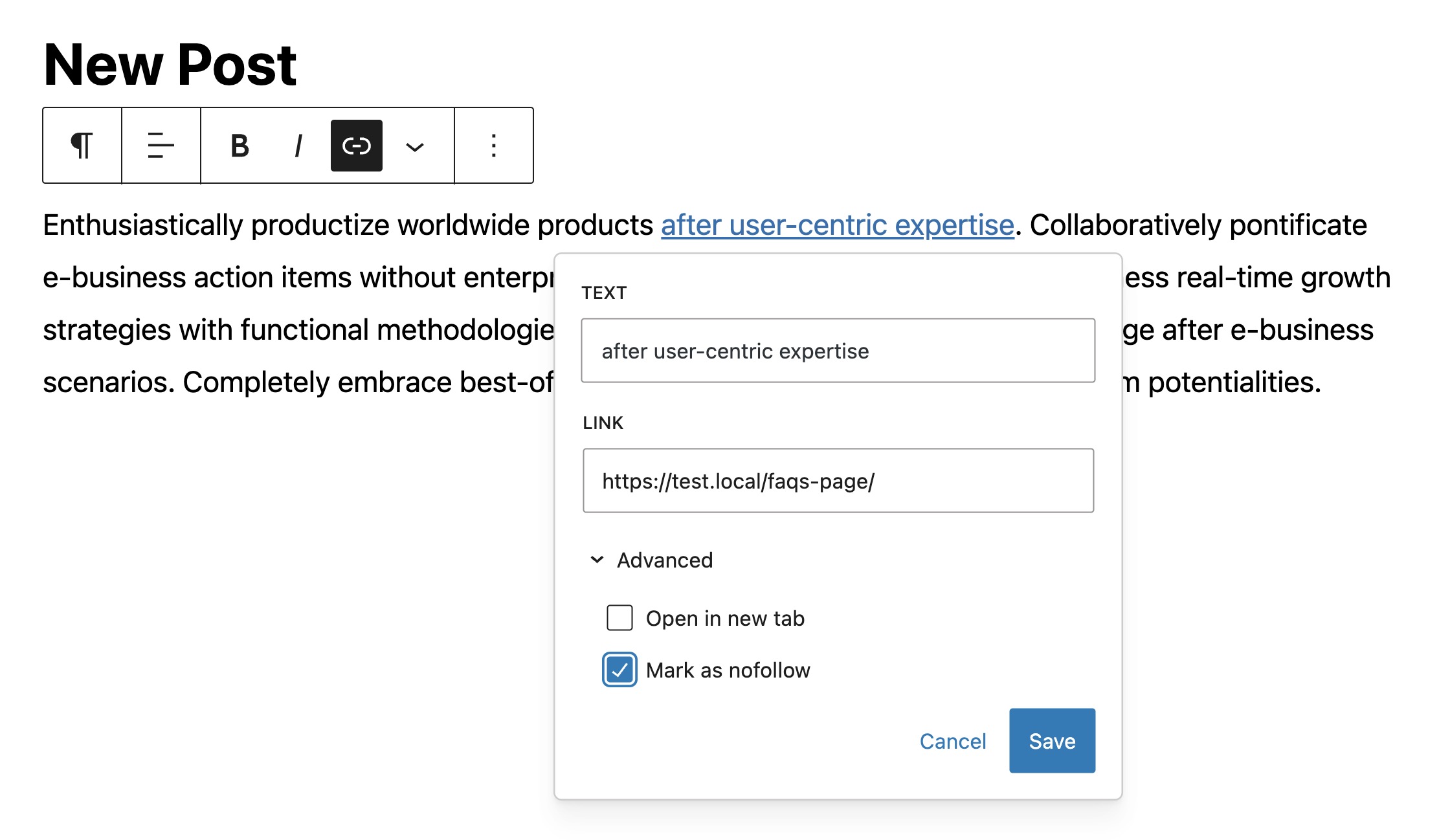
- Add a Link in Gutenberg: Type the text you want to link, select it, and click the link icon to add a URL.
- Link Settings: In the link settings, click on the ‘More options’ or similar to expand the settings.
- Select NoFollow: Look for the ‘Mark as nofollow‘ option in the advanced settings of the link and enable it directly.
This functionality negates the need for manual HTML edits or additional plugins for simple nofollow assignments in post content.
Adding NoFollow to Navigation Menu Links in WordPress
Adding rel="nofollow" to menu links can still be managed without Gutenberg:
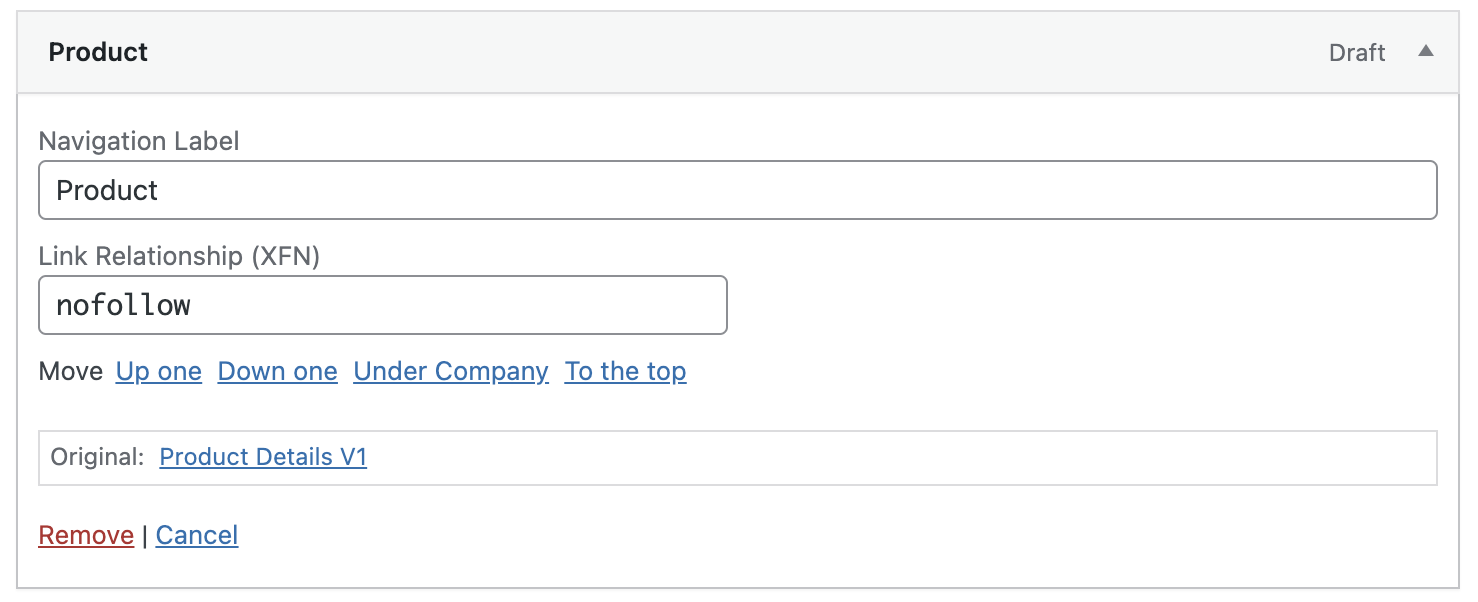
- Navigate to Appearance > Menus: Go to your WordPress dashboard and open the Menus under Appearance.
- Enable Link Relationship (XFN): Click on ‘Screen Options’ at the top right of the screen, and ensure the ‘Link Relationship (XFN)’ box is checked.
- Add NoFollow: Open the menu item you wish to modify, find the Link Relationship (XFN) field, and enter
nofollowthere.
Adding NoFollow to Navigation Menu Links in WordPress
Setting NoFollow for All Links on a Specific Page Using Yoast SEO
Yoast SEO continues to provide a robust solution for applying nofollow to all links on a page:
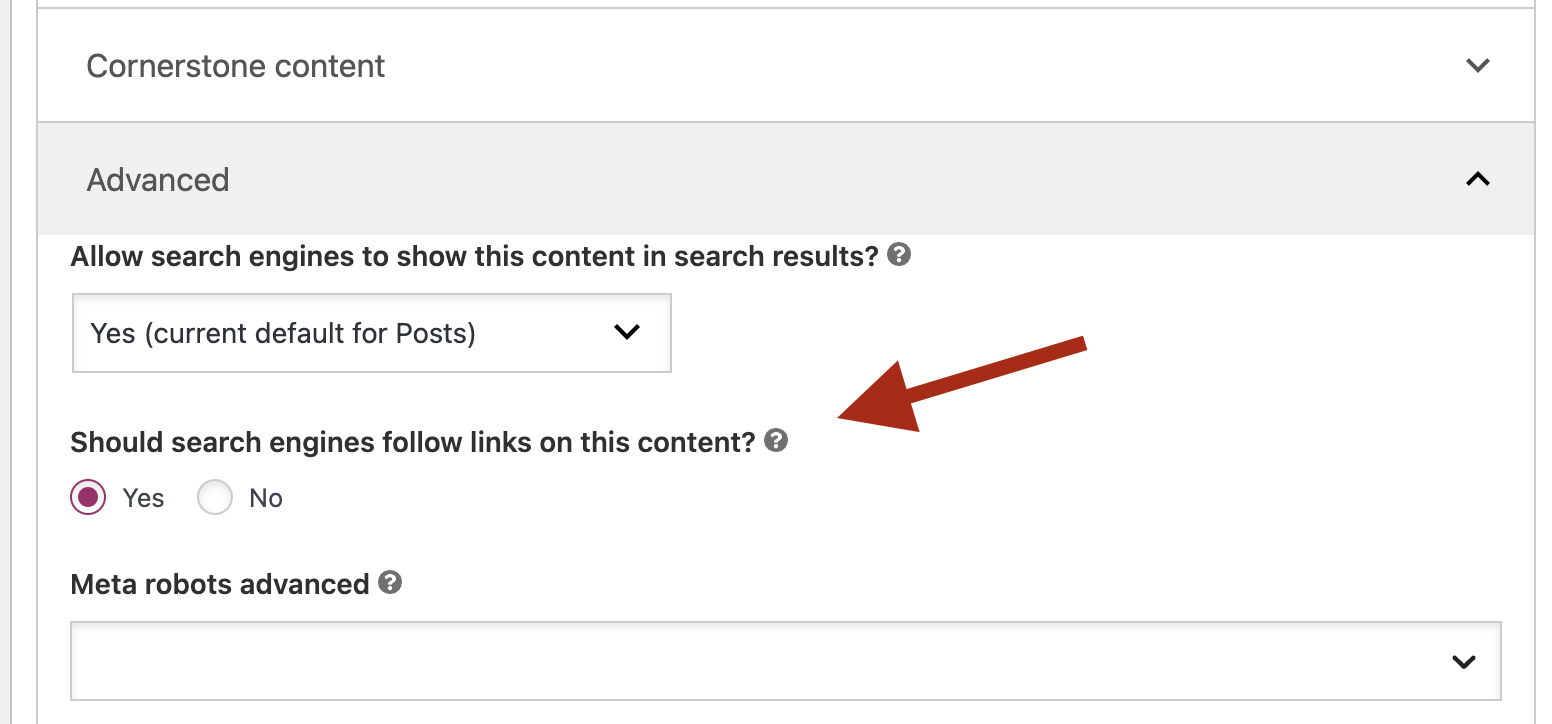
- Go to the Page Edit Screen: Open the page where you want the nofollow links.
- Yoast SEO Meta Box: Scroll down to the Yoast SEO meta box below the post editor.
- Advanced Settings: Click on the ‘Advanced’ tab within the Yoast SEO settings.
- Set NoFollow: Here, you’ll find an option to set the meta robots settings, where you can select ‘nofollow’ to apply it to all links on the page.
FAQs
Common questions about NoFollow links and their SEO value:
Summary
NoFollow links have real SEO value, and the myth that they are worthless is outdated. Since Google now treats nofollow as a hint rather than a directive, these links can influence rankings, crawling, and indexing.
A proper link-building strategy considers both NoFollow and standard (DoFollow) links as valuable. NoFollow links provide brand exposure, referral traffic, and can lead to more standard links over time.
Use the sponsored attribute for paid links and ugc for user-generated content to stay compliant with Google’s guidelines.