Outbound Links are the least appreciated tactic in Content Marketing and the process of On-Page SEO Optimization. Anyone involved in SEO undoubtedly knows that a link from the external world to your site is an important signal contributing to the page’s ranking in search engine results.
But did you know that outbound links from your site also hold significant value?
If you’re looking for a short answer without reading the post, then the answer is yes. Outbound links definitely contribute to page ranking assuming they are used appropriately.
In fact, outbound links are a crucial aspect for SEO and higher ranking. Outbound links provide additional value to readers, Thus, they enhance the user experience on your site. And as we all know, a good user experience implies a significantly higher ranking.
What Are Outbound Links Exactly?
As a starting point, and for those new to the field, outbound links appear like this:
<a href=”http://www.example-domain.com/”>Link Anchor Text</a>And since many tend to confuse between types of links (even experienced website owners), let’s explain the different types of links once and for all:
- Internal Links – These are links that lead from one page on your site to another page on your site. Here’s an example of an internal link in Savvy Blog.
- External Links – These are links that lead from one site to another. However, note that there are two types of external links:
- One is Outbound Links, which we’ll discuss in this post – these are links leading from your site to another site.
- The second is Inbound Links or Backlinks – these links come from another site and lead to your site.
In other words, an Outbound Link is a link from your site to another site. An Outbound Link from your site is an Inbound Link for someone else.
There are some misconceptions about outbound links, here are a few of them:
- It’s best to avoid adding outbound links since they send visitors away from your site, and you have no control over the content on the other side of the link.
- The best way to retain visitors on your site when using outbound links is to ensure they open in a new tab in the browser.
- You should always mark outbound links with the nofollow attribute to retain the page’s ranking value where the link appears (Link Equity).
So not only are these myths, but implementing some of them could lead to negative or less than ideal outcomes in the end.
The Importance and Implications of Outbound Links
Outbound links are one of the ways search engines discover new content. They are important as they enhance site promotion, build trust, and establish relationships with other businesses. Let’s elaborate..
1. Outbound Links Contribute to User Experience and On-Page SEO
Outbound links bring balance and authenticity to the general “health” of the page in terms of SEO. Consider this, professional or academic articles always reference sources. “Outbound links help establish authority just like professional articles adding references at the end.”
So, it’s easy to imagine how outbound links can strengthen the topic of your article for Google and other search engines. In a hypothetical scenario where all parameters are the same between two pages on different sites, it makes sense that a page with an outbound link to relevant content would perform better than a page without those links.
But what will be the actual impact of these outbound links on the page’s ranking in search results?? From an SEO tactics standpoint, outbound links definitely don’t carry the same weight as inbound links, and you could even say they are significantly less impactful.
2. Outbound Links Help Build Trust in Your Content
Discerning readers nowadays seek signals that your content is authoritative and reliable, and outbound links serve as signals in this context.
You should include outbound links to content in order to support and strengthen the points you are trying to convey through additional evidence and opinions. This action will make the content on your site appear more reliable and trustworthy. Additionally, adding outbound links demonstrates to readers (and even to Google) that you have researched the topic and are not solely relying on your own opinions.
3. Outbound Links for Building Relationships
Building a relationship system with other websites can be beneficial in various ways. For example, you’ll find that adding calculated outbound links within your content can encourage various experts from those sites to participate and engage with your content when you ask them to.
Adding outbound links provides an opportunity to reach the owners of the site you’re linking to and prepare them for the fact that you will be referring to them from your post. In this case, it’s likely that there will be a higher chance they’ll assist you in promoting the post and sharing it in relevant places.
In summary of this section, few people in our day think that adding outbound links isn’t necessary; however, debates still exist about the best way to do it…
Adding Outbound Links – Best Practices
Many websites follow their own guidelines about when and how to add outbound links. Sometimes, these guidelines evolve due to observation and tracking of actions taken by other content writers.
Creating guidelines in the context that are clear to your content writers will enhance the effectiveness and usability of those outbound links they add to the content.
A. When should you add an outbound link?
Content marketers generally use outbound links to provide quick access to information about relevant content they aren’t writing on their own site.
“Think of outbound links as a way to provide additional background on topics you can’t fully cover in your post.”
Here are some guidelines for adding outbound links:
- Use them to support claims or facts you present.
- Reference the source of the information (origin).
- Utilize them to illustrate a specific point or idea.
- Give credit to the article that helped you form an opinion on the subject you’re writing about.
- Add them when quoting a specific idea someone else wrote about before you.
B. How can you determine if a specific page you’re considering linking to is a good choice?
Note that the choice of where to send your readers is as important as the decision to send the user to another source at all. When choosing where to link, consider the following points:
- How relevant is the page you’re linking to the point you’re trying to convey?
- Is the content on that page written accurately and without errors?
- Does the page also provide sources for the information it delivers?
- Is it the original source of the information?
- Does the organization that created the page have a good reputation?
- Is the author of the page you’re linking to a reliable source?
- When was the content on the page you’re linking to published, and is it updated?
- Avoid linking to pages with many ads that could frustrate readers.
- Avoid linking to pages with a poor user experience.
- Perhaps needless to say, but avoid linking to pages with paid content or requiring additional action from readers, such as registration (Gated Content).
For instance, I’m trying to link to content written in the last twelve months…
C. What about outbound links to competitor websites?
While only a few brave souls provide outbound links to their competitors, some do so without concern. Neil Patel argues, for example, that by prioritizing the interests of his site’s visitors over his own interests, meaning linking based on content quality rather than destination, it ultimately leads (according to him) to many users returning to his content.
He also claims in the video that he feels Google understands better where to rank his site due to those links, and that it even encourages his competitors to link back to him.
D. How many outbound links should I include?
Various tests and case studies show a correlation between the number of outbound links and search engine rankings if used correctly. However, there is no absolute truth about the ideal quantity of outbound links, and it’s certainly not black and white.
The average number of outbound links expected, by the way, is 19, but many pages ranked at the top have 100 or more outbound links. Yet, that doesn’t necessarily cause these pages to rank high.
Of course, in this context, the post length or the amount of content on the page where you’re adding outbound links needs to be considered.
So, understand that there’s no “magic number” for the ideal quantity of outbound links. As always, the idea is to treat your users and readers on your site as aspects related to SEO. If you see relevance in adding an outbound link and it contributes to the user experience, add it without overthinking, and certainly don’t stop yourself because you think you already have a significant number of outbound links in your content.
E. Should outbound links open in a new tab?
Most website owners believe that outbound links should open in a new tab in the browser, but there are user experience experts who think differently. Personally, I prefer opening links in a new tab, as you see in sub-blog, but even in this case, there’s no absolute truth.
This means that I haven’t encountered research that shows opening outbound links in a new tab significantly increases the likelihood of users returning to your site and spending more time there.
6. Should outbound links be nofollow?
A few years ago, SEO companies adopted the “nofollow” attribute to address the concern that outbound links weaken a page’s “link equity” or “ranking power.” However, this issue was resolved long ago with a Google update released back in 2009.
In the following link, you’ll find a detailed post about what nofollow links are and when to use them.
Today, there are only very specific situations where outbound links should be marked with the “nofollow” attribute. Most of these cases fall outside the scope of typical outbound linking. Here’s a list of cases where it makes sense to add the “nofollow” attribute to outbound links:
- Blog comments – it’s rare for blogs to allow “follow” links in comments. This was, in fact, one of the main reasons why the concept of nofollow links was created.
- Social networks (for example, links to Facebook posts).
- Forums and user-generated content. There’s no real reason to invite Google to follow links like “register here” or “login”, areas Google’s crawler can’t access or index.
- Certain blogs and news websites.
- Various widgets.
- Press releases.
- Untrusted content.
- Paid links or sponsored ads. To prevent paid links from affecting search results (which negatively impacts users), these links must include the nofollow attribute*.
Note – there are newer attributes you can use, such as “UGC” (User Generated Content) and “Sponsored,” which indicate user or paid links. You can alternatively (and preferably) use those when appropriate. More information about these link types can be found in this post: The impact of Nofollow, Sponsored, and UGC links on SEO.
One of the biggest mistakes writers and content marketers make is marking all their outbound links as nofollow by default.
7. What about reciprocal linking – is it harmful?
Reciprocal linking occurs when multiple websites link to each other. Naturally, a certain number of mutual links between two websites is normal and even expected. However, excessive reciprocal linking or linking that appears unnatural or irrelevant to the content can lead to issues.
8. When should you avoid outbound links entirely?
There are two main situations where you should avoid using outbound links:
- In your site’s navigation menu (Navigation Links) – this can confuse users since they expect navigation links to lead to other pages within your site.
- On landing pages aimed at conversion, such as sign-up pages – although in some cases you may need to include an external link for user trust purposes.
Either way, both of these cases fall outside the scope of editorial content, where linking to relevant pages and external resources is almost always beneficial.
You may also want to style outbound links differently from internal links on your blog. Check the linked post to learn why.
Tracking outbound links in Google Analytics
By default, Google Analytics does not provide data on clicks to outbound links because it doesn’t automatically track events in Google Analytics 4. You’ll need to set this up manually.
You can do this in several ways, the first is via a script that reports directly to Analytics, and the second is through Google Tag Manager.
For more details on Google Tag Manager, check out the Beginner’s Guide to Google Tag Manager.
In this post, we’ll show how to do it by adding a code snippet to your WordPress site. Add the following code to your theme’s functions.php file (make sure to remove the opening PHP tag):
<?php
function track_outbound_links() { ?>
<script>
// listen for all clicks on anything. You could change document to a selector like #content to make it more efficient.
$(document).on('click', function( e ) {
// if this is a link, and the href does not contain our domain, it's an external link. Track it.
if( e.target.href && e.target.href.indexOf( window.location.hostname ) < 0 ) {
ga('send', 'event', {
eventCategory: 'Outbound Link',
eventAction: 'click',
eventLabel: e.target.href, // the outbound link URL will appear as the event label in GA. Find under Behavior -> Events -> Event Label
transport: 'beacon' // not supported in some versions of IE
});
}
});
</script>
<?php
}
add_action('wp_footer', 'track_outbound_links');
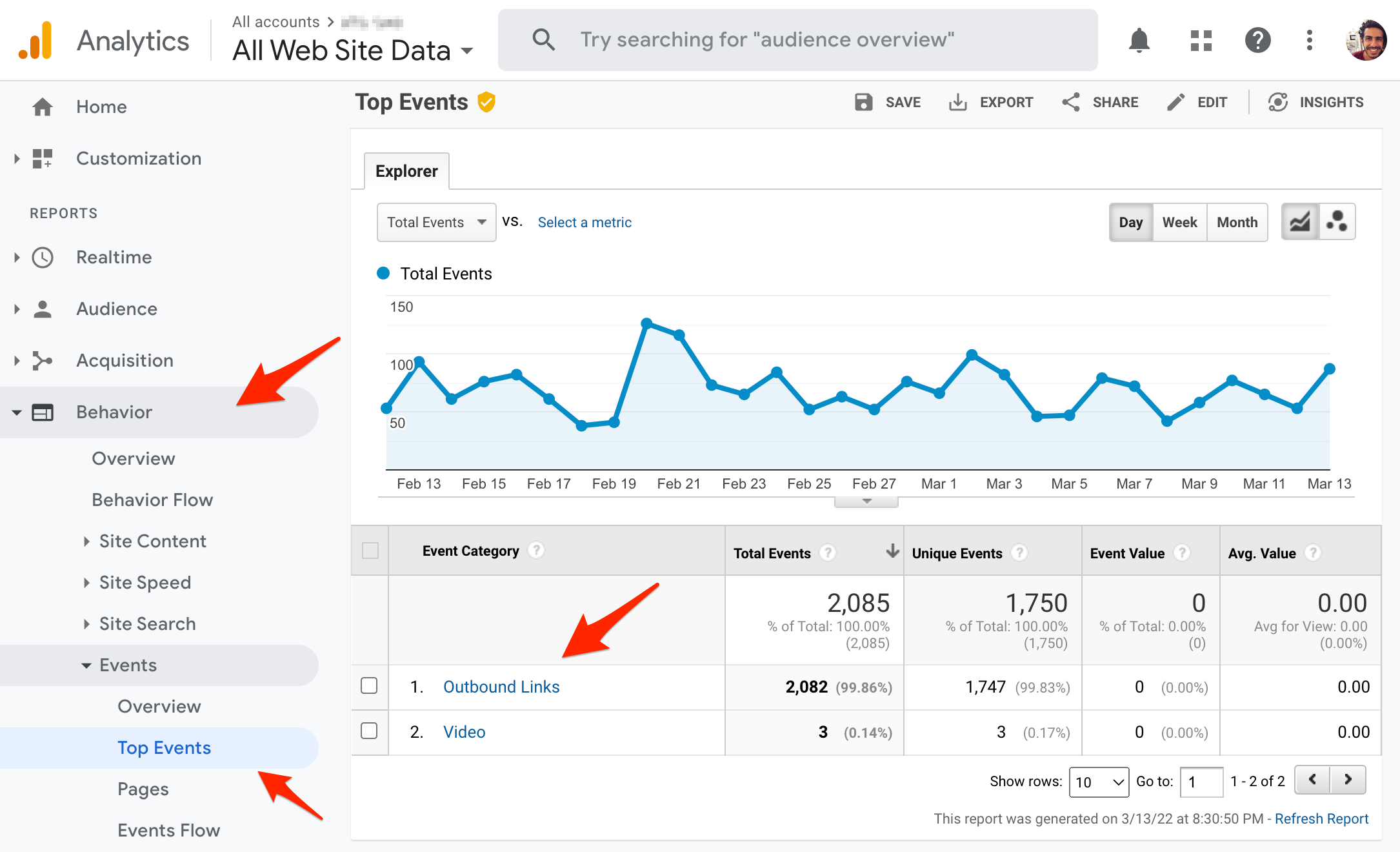
Now you’ll be able to see this data in Google Analytics under Behavior > Events > Top Events > Outbound Links.
Summary
Outbound links are an important way for websites to contribute to and enrich the internet as a whole. They add value to users, help improve your site’s credibility, and open opportunities for communication and collaboration with other businesses.
As you can see, there are quite a few factors to consider when it comes to using outbound links effectively. Some depend on the situation, such as assessing the trustworthiness of the linked source, while others are straightforward, like adding the “nofollow” attribute to sponsored content.
In conclusion, this post covered the most common questions about the best practices and proper use cases for implementing outbound links on your site.
Did you learn something new from this guide? Do you have thoughts or feedback about it? Feel free to share them in the comments below. Good luck!
Further Reading & Inspiration:



