Not long ago, a Savvy Blog visitor asked me whether they should redirect all pages that return a 404 error to the homepage. This question, along with other similar questions I encountered, made me realize that there’s a misconception about dealing with 404 error pages.
And even though it’s quite common and technically correct to call 404 pages “errors”, this terminology can be a bit problematic from our perspective, as 404 pages are the desired and intentional result (in most cases) when a website fails to return a specific request to the browser.
In other words, when a request is made to a URL that doesn’t exist on the server.
You could say that 404 pages are not errors but an integral part of the user experience – and you (as well as users) should understand this.
You Can Relax. 404 (Error) Pages are Completely Fine
So, 404 pages are actually fine, and there’s no need to panic. Also, there’s no need to redirect every page that returns a 404 error to the homepage, or to the category page that contained the same product that went out of stock.
Many times I’ve heard SEO experts recommend implementing a 301 redirect for each of those 404 pages in order to preserve the same Link Juice, meaning the same Google ranking, for that page/address. However, this is not the right way to handle these pages.
It seems people tend to fret about 404 pages because they’re concerned that Google might penalize their site if those pages exist. Conversely, they worry that the same strength an existing link possesses, the same Link Equity, will diminish when high-quality links point to 404 pages. The theoretical concern is valid for all opinions (more on that later).
In general, despite some exceptions, 404 pages are entirely normal on websites. There’s no need to worry about them, and at least for now, there’s no certainty or evidence that Google harms a site’s ranking simply because these pages exist.
To the contrary – Google mention that 404 pages does not have any negative affect on your SEO ranking.
404 errors do not affect your site’s SEO or its performance on search engines. You can definitely ignore these if you are sure that the URLs in question do not exist on your site*.
You should actually ensure that these and other invalid URLs return a 404 status code and, of course, that they are not blocked by the robots.txt file.
*So, in what scenarios are 404 (Error) Pages problematic?
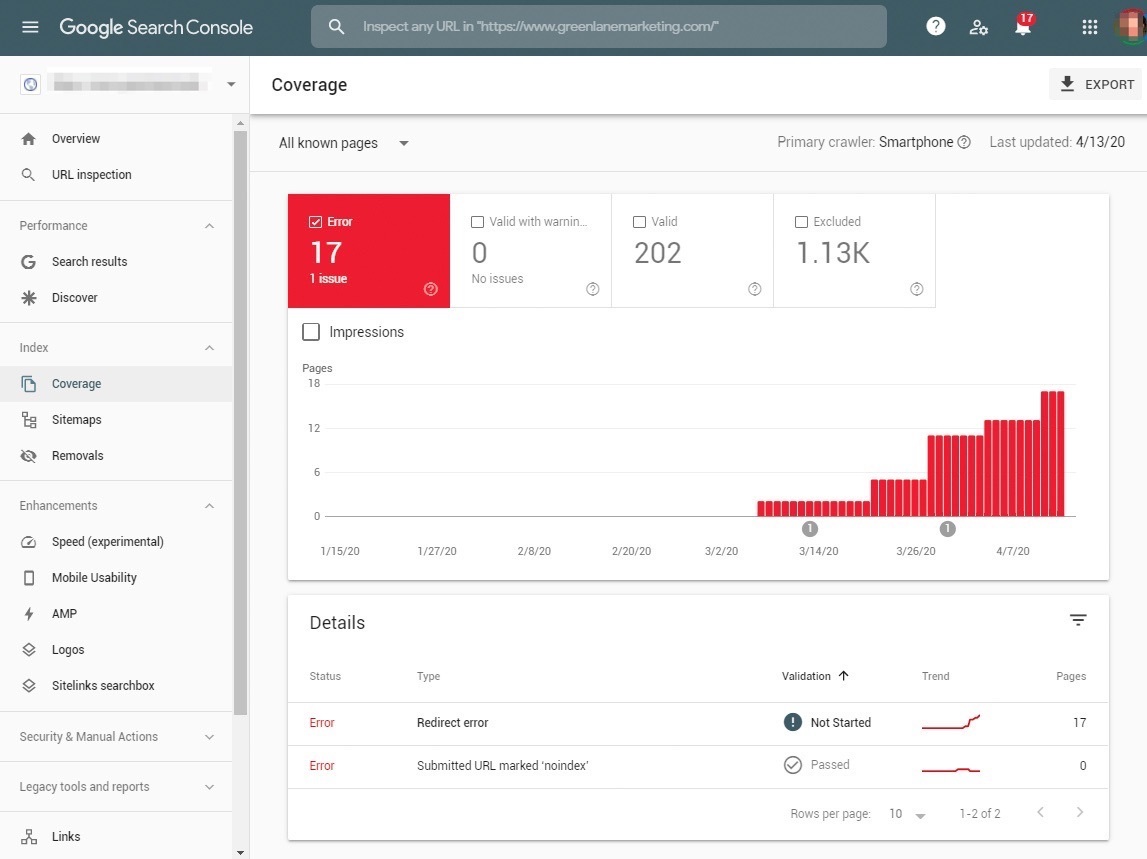
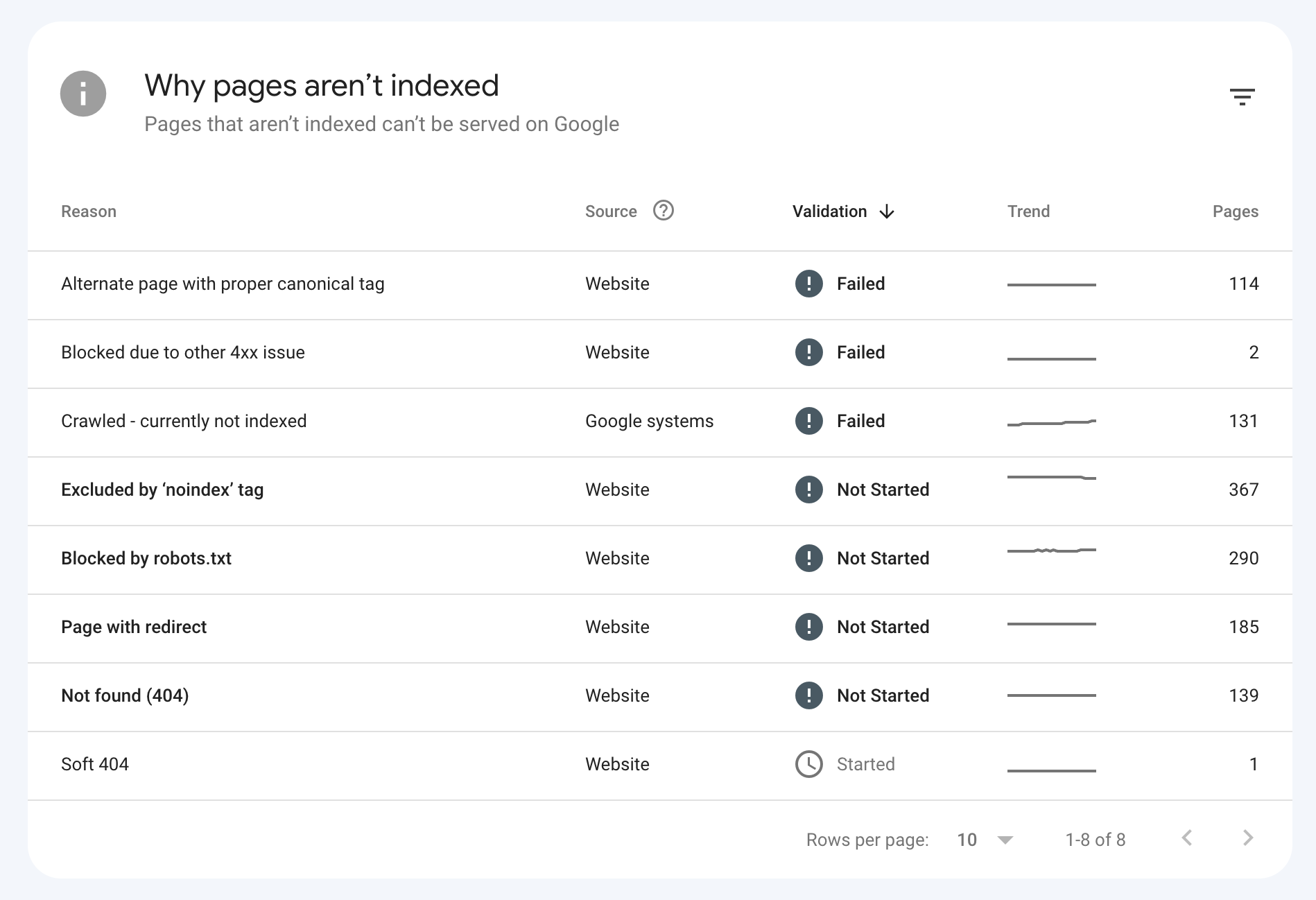
There are situations where your site’s ranking might be affected due to a high number of 404 pages. If there’s an abnormally high number of 404 pages, whether you see it yourself or through tools like Google Search Console, it likely points to a more significant issue with site crawling and technical SEO.
Of course, this situation doesn’t provide a good user experience, a state that probably affects your ranking across different search engines.
In many cases, continuously occurring 404 errors are not a positive sign. Forget about optimization and SEO for a moment, is it a good user experience for visitors on your site? Obviously not… Remember, search engines follow users. A good user experience significantly reflects on your site’s ranking.
Another potential negative implication of 404 pages is when there are high-value external links pointing to the same 404 page. Should you redirect to another page to preserve the link value? We would greatly appreciate hearing your thoughts on this matter.
Our opinion is that you shouldn’t hastily redirect every page that falls under this category. Instead, you should only do so if there’s a relevant match for redirection, meaning a relevant page in terms of content to that specific 404 page.
Despite this, another solution in these cases of valuable links is to contact the site owner where those links exist and ask them to update the link to a relevant page on your site. You can also create new content on your site that’s relevant to the existing link.
To conclude this section, the worst case with 404 errors is when they return a 200 status code. This condition is called Soft 404 and is not a positive situation because search engines continue to index these pages. Ensure that your server returns the correct status code for each type of page.
Take a look at the post that explains (in the context of 404) what to do with out-of-stock products in E-Commerce stores.
How to Actively Identify and Find 404 Errors on Your Site?
It’s important to be aware of 404 errors on your site, as well as outbound links that direct to pages with these errors on other sites. There are several free tools that can help you find these broken links more easily:
- Google Search Console – Any 404 errors that Google’s bot finds on your site will be displayed in Google Search Console under the Indexing – Pages section.

- deadlinkchecker – Enter your site’s URL and the tool will scan and report on 404 pages and broken links among other things.
- Broken Link Checker – This WordPress plugin will report broken links on your site, whether they’re outbound or internal links.
Common Causes of 404 Errors in WordPress
While 404 pages are part of any website, WordPress sites have their own unique triggers for these errors. Things like plugin conflicts, broken permalinks, deleted pages or posts, and issues with multilingual setups can often lead to unexpected 404s.
If you’re managing a WordPress site, it’s important to understand the specific reasons why 404s may occur, and how to properly resolve them. If you’re running a WordPress site, check out our full guide on WordPress 404 error causes and solutions , it covers the most common triggers and how to properly fix them.
How to Track 404 Pages in Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
Tracking 404 error pages in GA4 can help you identify broken links or missing pages on your site. Fortunately, GA4 provides built-in features to track these pages without the need for additional code. Follow these steps:
- Ensure Your 404 Page Has a Unique Title: To easily track 404 pages, make sure your 404 error page has a unique and descriptive title, such as “404: Page Not Found”. This title will help you filter and analyze 404-related data in GA4.
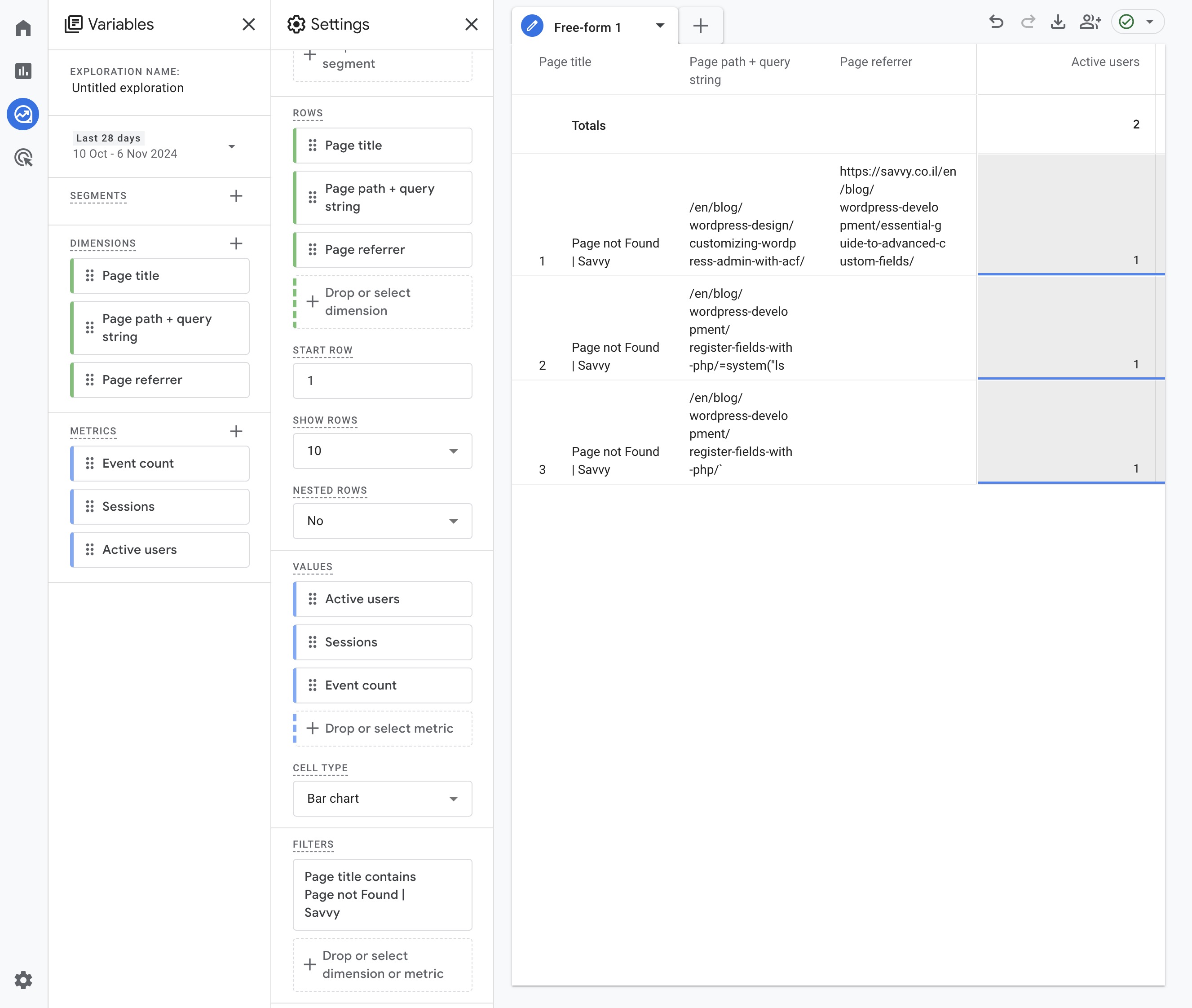
- Set Up a Custom Exploration for 404 Pages: Create a custom exploration:
- Navigate to Explore in GA4.
- Select Blank Exploration.
- Add Page referrer, Page path + query string and Page title as dimensions.
- Add Active users and Sessions as metrics
- Move or drag the newly added dimensions to Rows & metrics to Values.
- Filter the data by Page title and set it to contains “Page not found” (or your specific page title for 404 page).
- Analyze the Page path + query string to identify specific broken URLs.
Using these built-in GA4 features, you can effectively track 404 pages and address any broken links or missing content to enhance user experience.
Create a User-Friendly 404 Page
Some people think that the appearance of 404 error pages isn’t relevant because it’s the last place they want their website users to end up. However, creating a user-friendly or creatively designed 404 page can turn what might be a negative experience for the user into a positive one.
If you haven’t yet spent time on your website’s 404 page, now might be the time to do so, as it could be what encourages a user to continue navigating your site if they land on such an error page.
Sometimes it’s hard to imagine why there would be 404 pages on our site, but even if we think our site operates flawlessly, 404 pages are much more common than noted.
For example, you should ensure that your 404 page is beautifully designed. You can add a search option to those 404 pages, include a link to the homepage, etc. I’ve gathered a few examples of very creative error 404 pages that make you want to stay on the site:
- 404 error page on drible.com.
- 404 error page on dfy.co.kr.
- Error page 404 on spotify.com.
- Error page 404 on kualo.co.uk.
FAQs about 404 Error Pages
To Summarize
So, in summary, there’s no need to worry. 404 pages are entirely normal, as explained in this post. If you’re looking for a concise summary, here are the key points regarding redirecting 404 pages that we discussed in this post:
- Do not perform automatically redirects to all 404 pages.
- Do not globally redirect 404 pages to the homepage.
- Redirect a specific 404 page to a relevant category or parent page only if this redirection provides the most relevant user experience for the visitor.
- It’s perfectly fine and actually necessary to serve a 404 to the visitor when the page no longer exists.
- Ensure that the robots.txt file does not block 404 page URLs or invalid URLs.
- If there are valuable links pointing to 404 pages, use one of the tactics we discussed earlier.
- Create a user-friendly 404 page.
- Read our detailed guide on WordPress-specific 404 errors to understand and prevent common issues.
For more information. Good luck!