The topic of On-Page SEO and Content Optimization stands on its own. However, before you touch the website content, it’s likely and right to perform actions related to Technical SEO as discussed in the first part of the series.
But remember, as mentioned at the beginning of the guide, in the process of On-Page SEO, you must first and foremost consider the visitors to the site and a proper user experience, and only then how the various search engines will see the content.
You should treat Google and search engines as users visiting your site. Technical optimization (Technical SEO) along with improving the user experience and writing content that provides value to visitors will certainly lead to a higher ranking on Google.
So, let’s talk about that content optimization and start by explaining to those who don’t know what On-Page SEO actually is. Enjoy the read! 🙂
What is On-Page SEO?
On-Page SEO (sometimes called On-Site SEO) is the process of optimizing individual pages and site content, designed to improve the site’s ranking on search engines and attract more relevant visitor traffic.
The process refers to the optimization of content as well as the optimization of HTML markup, as opposed to the process of Off-Page SEO which relates to backlinks from other sites and external signals, and as opposed to Technical SEO that focuses on making it easier for search engines to crawl and index your site. Take a look at the following diagram:
As you can see, there are no clear boundaries between Technical SEO, On-Page SEO, and link building; they work together to achieve full SEO optimization.
However, it can be said that On-Page SEO mainly involves making changes to various aspects of content. When we look at these changes individually, they might seem like small steps, but the combination of those steps along with valuable content for users and technical SEO will undoubtedly lead to higher rankings in organic search results.
You need to think of these steps as improving the user experience on your site. From the user’s perspective, the more interaction and engagement with the content, and the longer they stay on the site, the better the user experience will be.
Google Site Optimization – Content Optimization | On-Page SEO
Likely, creating informative and valuable content will have the most significant impact on your site’s ranking in Google compared to other factors mentioned in this guide. Users can recognize quality content, and they will probably want to refer others to this content. These referrals can come through other blogs on the same topic, social networks, emails, forums, and other means.
Organic sharing or word of mouth are what will help you build your site’s trust and authority (E-E-A-T) among users and Google, which doesn’t happen without original and quality content. The goal of content optimization and On-Page SEO is to make the content relevant to what users are searching for and present it appropriately in search results.
A. Keyword Research
In a world where optimization practices are constantly changing, one thing remains quite constant: the need for keywords and keyword research.
As marketers, you need to be familiar with the various tools that allow you to choose the most suitable keywords for your business. Remember that you should approach keyword selection with different strategies in mind, but don’t rely on these tools too much.
Keyword research doesn’t start with these tools; it starts with understanding your target audience. These are the people and the population that will be searching for your content, so it’s critical to understand their demographic data, their areas of interest, and their needs.
After understanding and identifying your target audience, the next step is to segment this audience into smaller groups and create segments based on needs, demographic data, and various areas of interest. Why? Because different people in your target audience will be looking for different things, and you want to cover all those people.
For example, people who simply browse and are interested will use words like “best,” “review,” “top 10,” and similar. On the other hand, people who are looking to buy a product will use terms like “buy,” “discount,” and “affordable.”
This categorization is important because Google values user intent when ranking search results. If Google identifies that a certain search query contains an intention to make a purchase, the search results will likely favor e-commerce sites, as the user is looking to buy a specific product.
Google doesn’t use a fixed character count to decide title or meta description length. Both can be truncated in search results based on pixel width, not character count. The character recommendations below are practical guidelines to avoid truncation, not hard rules.
So, after understanding your target audience and finding the right keywords and phrases for your business, and before we describe some practical ways to improve your On-Page SEO, take a look at the following image that illustrates the basic components of a Google search result:
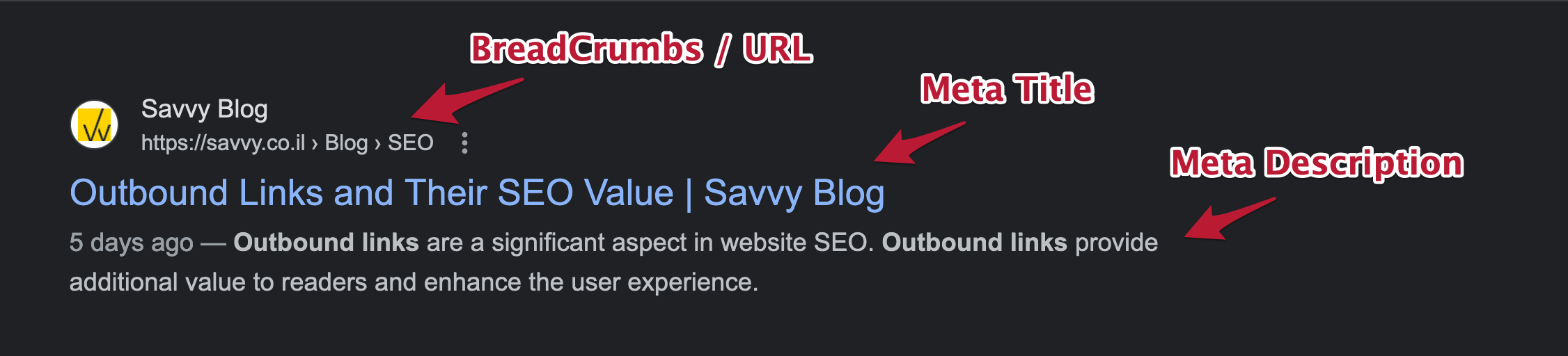
B. Create Unique and Precise Page Titles – Title Tag
The Title tag is essentially the page title and indicates to both users and search engines the subject of a specific page. This tag should be placed within the <head> section of the HTML document.
<title>Primary Keyword - Secondary Keyword | Brand Name</title>
If your page appears in search results, the content of this tag will likely appear in the first line of the result itself. For example, the homepage title can mention your site/business name and may also include additional important information, such as the physical location of the business or primary domains/products of the business.
Be very considerate when choosing the title as it carries significant weight when search engines analyze the topic of the content you’ve written.
Writing Meta Title – Key Points
- Aim for 50-60 characters. Google truncates titles based on pixel width, but 50-60 characters is the practical sweet spot to avoid truncation.
- Optimal structure – Primary Keyword – Secondary Keyword | Brand Name.
- Ensure that each page has a unique title.
- Front-load important keywords at the beginning of the title.
- Avoid titles that excessively stuff keywords for the sake of SEO.
- Write a title for customers – a title that catches the eye will generate more clicks.
- Align your H1 heading with the title tag for consistency.
This is the place to mention that the “Site Title” that you can set under the admin interface > Settings > General (or via Appearance > Customize > Site Identity) is different from the title tag in question.
That same site name is usually relevant only at the display level on your site and does not affect search engines and SEO. Either way, you need to correctly define both the site name and the site description, as these will later serve you as variables in various SEO plugins.
3. Create an Accurate Page Description – Meta Description Tag
The meta description or Meta Description Tag provides a summary of the page’s content. This is the description that appears below the title in Google search results. While the Title Tag we mentioned in the previous section should include a few words or a combination of words, the page description should include a sentence or two, or even a short paragraph.
<meta name="description" content="This is an example of a meta description. This will often show up in search results.">
Write a description that provides information and arouses interest among users if they see this description in search results, and make sure the text is long enough to appear fully in search results. Note that the main goal in writing this summary is to provide value and lead to a higher Click-Through Rate (CTR).
Furthermore, it means that you can and even should use the Meta Description to present solid facts about the page. For example, if it’s a page displaying a product for sale, you can include information in the Meta Description about the book’s author, its price, the book’s illustrator, and the like, all presented as clear and organized facts. Here’s an example:
<meta name="description" content="Written by A.B. Joshua, illustrated by Van Gogh, price: ₪17.99, length: 784 pages">
Writing Meta Description – Key Points
- Aim for 120-160 characters. Google may truncate longer descriptions, though it reads the full tag.
- Optimal structure – ideally, it should contain keywords but primarily be catchy and encourage clicks.
- It doesn’t have to be in sentence format; it can contain information and facts about a product or any News Post.
- Ensure a unique and distinct description for each of your site’s pages.
- Avoid using quotation marks for the entire text.
- Avoid writing keyword-only descriptions for SEO – it won’t achieve much.
4. Proper Use of Heading Tags – H1, H2 Tags
Since heading tags are usually bold and have a larger font size, they provide an important visual clue that indicates to users and search engines what the content under that heading is about. These headings also contribute to higher readability for users.
<h1>H1 Tag</h1>
Some Text
<h2>H2 Tag</h2>
Some Text
<h3>H3 Tag</h3>
Some Text
<h2>H2 Tag</h2>
Some Text
<h3>H3 Tag</h3>
Some Text
<h4>H4 tag</h4>
Some Text
To create a proper hierarchical structure of content, use various heading tag sizes that allow users to easily scan the document. Think about the content’s interests and identify key points and subpoints in the page’s content. As a result, decide where you want to use H1, H2, H3 tags, and so on.
Heading Tags …H1, H2, H3 – Key Points
- Maintain hierarchy in heading tags, with each heading level progressing in an orderly manner from a larger heading size to a smaller one.
- Avoid placing text in heading tags that is not useful for defining the page’s structure.
- Don’t use heading tags in places where other tags like
<em>and<strong>are more suitable. - Avoid excessive use of heading tags on a page.
- Avoid very long headings.
- Use heading tags for structural presentation, not for text styling.
- Using more than one H1 tag is technically valid, but keeping a single H1 per page is best practice for clarity.
- In most sites, the text of the H1 tag matches the Title Tag.
In summary, proper use of heading tags and hierarchy plays an important role in improving your site On-Page SEO. Make thoughtful choices in your selections.
For more information on using heading tags, you can find in the guide WordPress Heading Tags: How and Why to Use H1, H2. Although the article’s title mentions WordPress, the guide is relevant for any website.
5. Don’t Neglect Category Pages
In general, category pages on your site are more important than individual posts and pages. If you have a blog and you write several posts on a specific topic, the category page for that topic should be ranked first.
All the above applies to tags if they exist on your site.
Proper organization of categories is highly meaningful for Google to understand the different parts of your blog and interpret accurately what they are about. Take a look at the next post that talks in detail about Optimizing WordPress Categories for SEO to rank them higher in Google and search engines.
Category Page SEO – Key Points
- Give categories accurate names – you want the category name (Meta Title) to precisely describe what all the posts in that specific category are about.
- Don’t forget a short description for the category (Meta Description) – you’d be surprised how many times I come across sites that don’t provide a short description for a category.
- At the beginning of the category page, provide a description of 150-300 words that elaborates a bit more on what the category is about.
- Add 2-3 links to strong posts at the beginning of the category. These can help users quickly reach the desired content. Naturally, you want users to arrive at one of the posts through the category page and not leave the page.
- Make sure there are no duplicate names for categories.
6. Optimize Images Properly
An important action in the optimization of content for search engines is optimizing images. They are valuable SEO assets that should be utilized when possible. Images enhance the user experience by adding interest for visitors.
A carefully selected image grabs users’ attention more than text does. Images should emphasize the article’s subject and reflect the surrounding text. I won’t elaborate further as I’ve already written an article on Optimizing Images in the Context of SEO; take a look.
Image Optimization – Key Points
- Select a suitable image that reflects the surrounding text or the article’s subject.
- Choose a file name that matches the image file and reflects the image’s subject in a few words.
- Ensure the image’s dimensions match how it will be displayed on your site.
- Reduce the image’s file size.
- Add a caption if necessary.
- Use alternate text (Alt text) for each image, both for search engines and for users with disabilities.
7. What else can be done in terms of content to improve your ranking on Google?
There are several additional points I haven’t mentioned in the context of content optimization that are just as important. Here are additional points you should consider:
- Add relevant external links in your content that direct to other sites providing information relevant to the post topic you’re writing about.
- There is no specific recipe for keyword density in content. Write naturally about the subject and don’t try to force keywords. Excessive use of specific phrases or identical keywords can lead to a drop in ranking.
- Use rich media. Videos, graphics, surveys, and the like contribute to SEO as they keep users on your site for longer.
- Social sharing buttons can help amplify your content’s reach. While social signals are not a confirmed direct ranking factor, more visibility often leads to more backlinks and engagement.
Do you need an SEO expert to improve your rankings?
An SEO expert is a person with independent knowledge or someone who has undergone training to improve website visibility on search engines.
This guide provides you with a good amount of knowledge (hopefully), so you can venture on your own and perform content optimization efficiently. However, despite this, it’s advisable to consider hiring an expert for search engine optimization – someone who can assist you in examining the pages on your site.
Make sure to assess the potential benefits of hiring an SEO expert, as well as the potential harm to your site in case of irresponsible SEO management.
Many SEO experts offer useful services to site owners, including:
- Reviewing site content and structure and providing improvement recommendations.
- Technical consulting on website development topics, such as hosting servers, proper redirects, 404 error pages, and the like.
- Content development and writing.
- Managing online business development campaigns.
- Keyword research.
- SEO training.
- Expertise in specific markets and geographical areas.
If you’ve decided to hire an SEO expert, you should know that it’s better to do so early on so you can work together to ensure the site is search engine-friendly. However, before seeking an SEO expert, it’s wise to act as an informed consumer and learn how search engines operate.
Despite what’s been said, remember that initially performing technical SEO on your site to allow Google to crawl it properly is recommended. Only then should you focus on links and invest in content and user experience.
FAQs
Common questions about On-Page SEO and content optimization:
In Conclusion
Every SEO strategy focuses on achieving the highest possible ranking on search engines. To do that, you need to design and develop a site that Google’s algorithms will favor, through technical SEO, and then perform content optimization and On-Page SEO.
This guide aims to cover all aspects of On-Page SEO and content optimization for effective SEO and higher ranking on Google. But if we try to sum up this topic in a few words, it’s all about high-quality content and excellent user experience.
Both of these, along with technical SEO, will undoubtedly lead you to higher positions in Google search results. In conclusion, there’s no single winning recipe, only recommendations. However, I hope this guide helped you better understand this topic and those recommendations.
One last thing – if you’re using WordPress as a content management system, you’re probably relying on an SEO plugin like Yoast or Rank Math for many of the actions covered in this guide. If so, I recommend checking out my detailed guides on Yoast SEO and Rank Math.
You’re welcome to share the guide, ask questions, and provide constructive feedback in the comments below, as usual… 🙂


